Start Using PagerDuty Today
Try PagerDuty free for 14 days — no credit card required.
This integration requires use of our v1 REST API which was decommissioned on October 19, 2018.
For more information about the v1 REST API decommissioning, take a look at our FAQ here: https://v2.developer.pagerduty.com/v2/docs/v1-rest-api-decommissioning-faq
Please contact SaltStack to inquire about the status of this upgrade.
SaltStack is the leading systems management framework that combines remote execution with a wide range of other capabilities, from configuration management to server automation to monitoring services.
This Document details how to configure the remote execution and configuration management tools in SaltStack to be used with PagerDuty. A more detailed walkthrough of SaltStack itself can be found here.
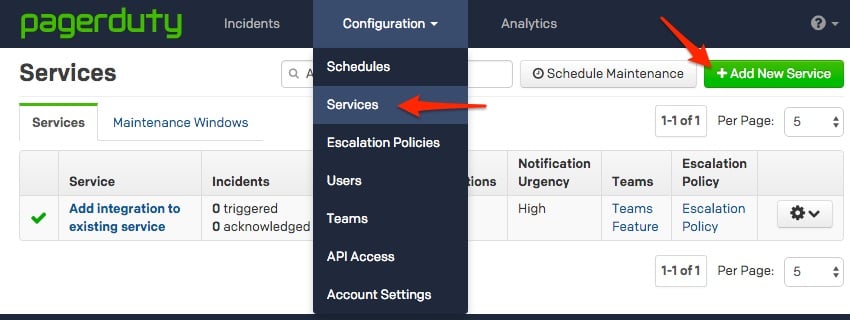
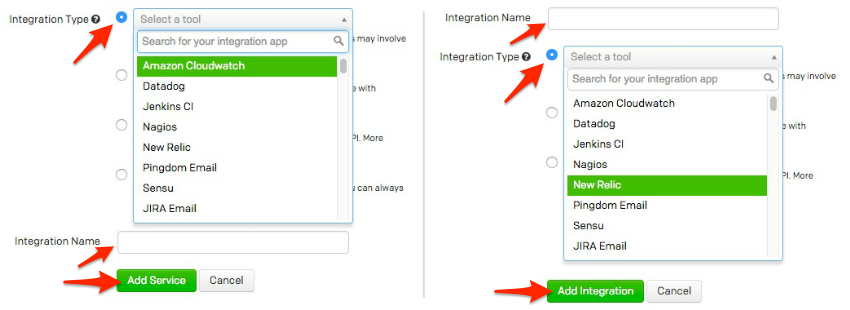
All PagerDuty PlugIns for SaltStack require the pagerduty subdomain and api_key, and an integration to be configured.

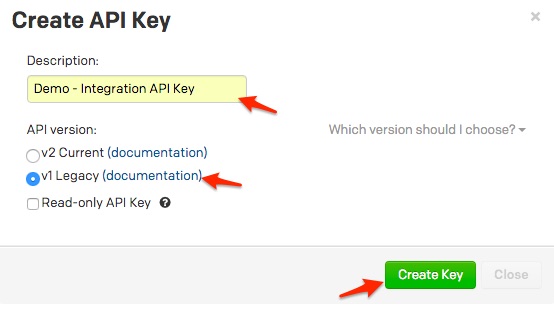 A note about versioning: API v2.0 is designed to make it easier for new integrations to communicate with PagerDuty. Most existing PagerDuty integrations will require an API v1.0 key. If you have questions on which API version to use, please contact support@pagerduty.com
A note about versioning: API v2.0 is designed to make it easier for new integrations to communicate with PagerDuty. Most existing PagerDuty integrations will require an API v1.0 key. If you have questions on which API version to use, please contact support@pagerduty.com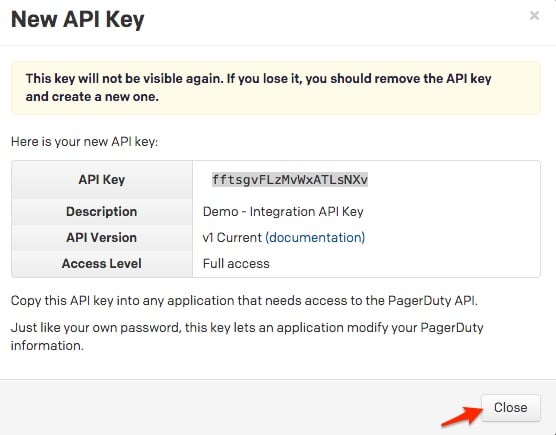
As of the 2014.7.0 release of Salt, PagerDuty is natively supported and requires no additional plugins. However, Salt must still be configured to use the PagerDuty modules. Currently, only minion-side functionality is supported.
Minion Configuration File
/etc/salt/minion file, to include the information from above. Assuming that your PagerDuty account is set to use http://myaccount.pagerduty.com/ and the above settings, the configuration stanza will look like:
my-pagerduty-config:
pagerduty.subdomain: myaccount
pagerduty.api_key: K42pPqY75U1Qr7e9
Pillar Configuration
PagerDuty can also be configured from Salt’s pillar system.
/srv/pillar/pagerduty.sls file, to include the information from above. Assuming that your PagerDuty account is set to use http://myaccount.pagerduty.com/ and the above settings, the configuration stanza will look like:
my-pagerduty-config:
pagerduty.subdomain: myaccount
pagerduty.api_key: K42pPqY75U1Qr7e9
/srv/pillar/top.sls file, to match the necessary minions to the PagerDuty configuration. Assuming all minions will be using PagerDuty, this may look like:
base:
‘*’:
- pagerduty
PagerDuty is available as an execution module, meaning that it is usable from the Event Reactor system inside of Salt. This guide has an example for using the basic event execution module. For a more complete discussion of the reactor system, see http://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/topics/reactor/.
/etc/salt/master file on the master. If it is not already present, add a section called reactor. In this section, add the name of the custom tag that we will use, and the location of the reactor file that will be used.
reactor:
- ‘my/custom/tag’:
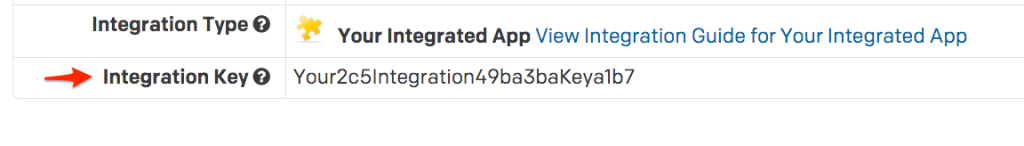
- /srv/reactor/my-custom.sls/srv/reactor/my-custom.sls. This file will instruct a minion called alertminion to trigger an incident in PagerDuty. Note that the service_key refers to the integration key mentioned above.
new_custom_alert:
cmd.pagerduty.create_event:
- tgt: alertminion
- kwarg:
description: “Custom alert from {{ data[‘name’] }}”
details: This is a custom alert
service_key: 8eb116b11626346239365c9651e
profile: my-pagerduty-config# On systems still using the legacy SysV init
service salt-master restart
# On systems using systemd
systemctl restart salt-mastersalt myminion event.fire_master '{"data":"my event data"}' 'my/custom/tag'</ol
It is also possible to create an incident during a state run. The following is an example that assumes that no state tree currently exists. A detailed discussion of Salt States can be found at http://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/topics/tutorials/index.html#states.
/srv/salt/top.sls that targets all minions with a state that monitors load average.
base:
‘*’:
- loadavg/src/salt/loadavg.sls that performs the load average monitoring. If the load average falls outside of the specified range, then an incident will be triggered in PagerDuty.
check_load:
status.loadavg:
- maximum: 1.2
- minimum: 0.05
- onfail:
- pagerduty: loadavg_trigger
loadavg_trigger:
pagerduty.create_event:
- name: ‘Bad Load Average’
- details: ‘Load average is outside desired range’
- service_key: 8eb116b11626346239365c9651e
- profile: my-pagerduty-configsalt myminion state.highstateOther functions are also available via the PagerDuty execution module. To use these functions, at least one minion must be configured for PagerDuty. The current release of Salt supports listing incidents and current services.
Listing Services
In addition to the other information returned, this function will return integration keys which can be used to trigger incidents. To make a call from the master, using a configured minion:
salt myminion pagerduty.list_services my-pagerduty-configListing Incidents
This function will return all incidents associated with this account, including open, acknowledged and resolved. To make a call from the master, using a configured minion:
salt myminion pagerduty.list_incidents my-pagerduty-configTry PagerDuty free for 14 days — no credit card required.